Ultrasound Video Summarization using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Super Short Introduction
- Paper Link
- This paper selects few mutually disjoint but temporally contiguous chunks of frames from input video as summary. Idea is applied on Ultrasound fetal screening videos. Novelty of the paper is that the training can be done in both supervised as well as unsupervised way and that it uses RL (reinforcement learning) for it.
Feature Extraction
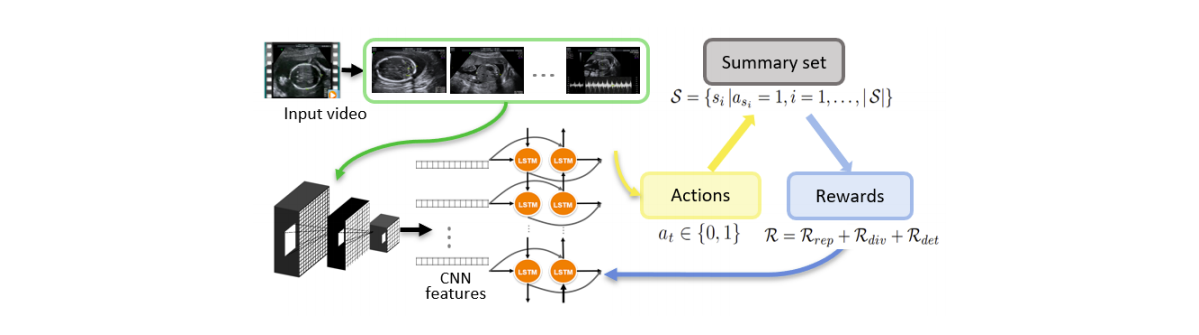
A pretrained diagnostic view plane detection network is used for feature extraction. Its weights are not updated during training. Each frame is passed through the feature extraction network to yield feature maps. These are subsequently aggregated using a bi-LSTM module.
RL setting
- Input: Output of the bi-LSTM for each frame.
- Action \(a_t\): For every frame, a boolean decision is to be made: Whether to include it in the summary or not.
- Reward: It has multiple components. \(R_{det}\) determines the likelihood of a summary’s frame being a standard diagnostic plane. \(R_{rep}\) defines how much summary frames are representative of the entire video. \(R_{div}\) ensures diversity within the summary frames.
- In \(R_{rep}\), for every frame of the video, it finds most similar frame present in the summary \(S\) with which it finds the distance. This component is simply the average of the distance over all frames of the video.
\[R_{rep} = exp(-1/T \sum_{t=1}^T \underset{t'\in S}{min}||x_t - x_{t'}||)\]
- In \(R_{div}\), diversity among the selected frames is maximized. Cosine similarity is used to measure the difference between two frames.
- In \(R_{det}\), inclusion of frames which are classified as diagnostic view plane are encouraged. Note that this depends upon the goodness of the classifier.
- For supervised setting, another term \(L_{Pred}\) is introduced in the loss. It is aimed to minimize the difference between ground truth importance scores and the predicted importance scores for each frame.