A Hierarchical Generative Model for Eye Image Synthesis and Eye Gaze Estimation
Super Short Introduction
- Paper Link
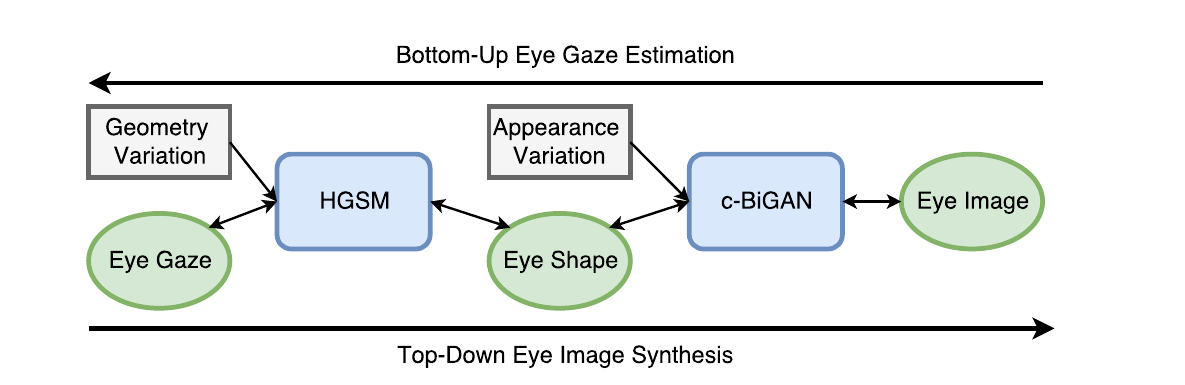
- Novelty of the paper is the dual ability to estimate gaze from image and generate image given gaze and geometric inputs. They introduce an intermediate state of image shape. Image shape ( representation of eye using discrete dots) is generated from input Image using c-BiGAN which is a GAN and is therefore learnt using data driven approach. HGSM is used to predict Gaze from the image shape. It uses the geometric knowledge of eye and it’s methodology is based on the standard 3D model of the eye.
An Overview of the Methodology
Definitions:
- Eye shape: A visual representation of eye made using discrete points. In this representation, when compared with input image, texture and other appearance based effects are removed. Eye shape contains purely geometric information and therefore is analytically and faithfully generated given the gaze and person specific parameters.
- ECS: Eye co-ordinate system
- CCS: Camera co-ordinate system. Note that head pose {R,e} is the rotation and translation matrix in ECS which converts to points to CCS.
HGSM
As noted above, Eye shape contains purely geometric information. HGSM uses the standard 3D eye model. After taking kappa and eye radius as input, 3D eye is generated. It is then projected onto the 2D plane to generate the eye shape. Following are the various steps involved for the generation of eye shape from gaze and person specific geometric parameters:
- Kappa (\(\theta_k,\phi_k\)) and eye radius (\(r_o\)) is sampled from their respective priors.
- Visual axis and Optical axis are drawn (having angle kappa between them)
- Pupil center is drawn in ECS using above parameters. Head pose is used to get pupil center IN CCS.
- Using a linear model with noise allowing shape variations, iris and eyelid contour co-ordinates are obtained in ECS. Gaze is the dependant variable here. Similar to pupil center, convert them into CCS using head pose.
- Finally, using camera projection matrix W, get their co-ordinates on image frame. this gives us the eye Shape.
Conditional BiGAN
This is inspired by conditional-GAN and bidirectional-GAN. Generator (G) takes eye shape and a random vector as input and generates the eye image. Another component Encoder (E) takes in the eye image and generates the eye shape. Finally, Discriminator (D) takes in eye shape and eye image as input and predicts 1 when both of them are consistent with each other.